What do Model Train Scales, Rail spacing, Rail Height, and Track Code, Fishplate / Joiner mean?
The scale shows the reduction ratio according to the reality of the model. The use of model products that are reduced/produced using the same scale will ensure that the model area created is accurate and realistic.
There are many generally accepted scale values in the world as well as different scales used by smaller groups. Scales can be represented as numerical proportions (eg 1/87), mostly expressed in letter codes such as HO, OO, N, TT, and Z as determined by the standards. NEM and NMRA standards are decisive for the scales and standards established by these institutions.
The scale indicates the reduction ratio between the real and the model. A model locomotive with a 1/87 scale or HO scale is the fact that its reality is reduced by 1 in 87. If we give an example, the HO scale model of a wagon, which is actually 10 meters tall, will be 11.5 cm in length.
Rail spacing (Gauge) is the distance between two iron rails forming a line on the railway. In most railways in the world, this distance, which we will call the rail spacing, is 1,435 meters (1435mm). When we look at the HO scale, this length corresponds to 16.5 mm (1.65 cm).
For many scales used in model training in its historical development; You can use the table at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_transport_modelling_scales
Almost all scales used in modeling are listed at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_scale_model_sizes
Here are some examples of some scales that manufacturers use popularly.
| Code | Rate | Rail Range |
| Z | 1:220 | 6.5mm |
| N | 1:160 | 9mm |
| TT | 1:120 | 12mm |
| HO | 1:87 | 16.5mm |
| OO | 1:76 | 16.5mm |
| On30 | 1:48 | 16.5mm |
| O | 1:45 | 32mm |
| 1 | 1:32 | 45mm |
Model train scales comparison chart
You can take advantage of the image below for locomotives and wagons for HO, TT, N, and Z.
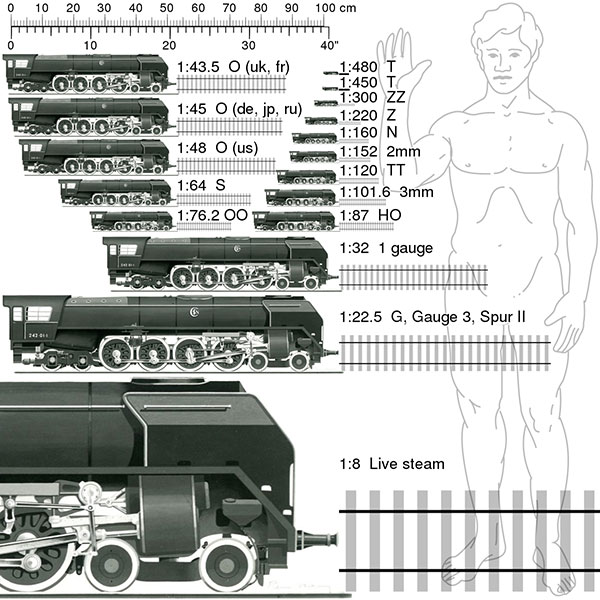
Different sizes can be seen on HO-OO-On30 models using the same rail spacing. It is thought that there is a serious difference, especially between OO and HO. However, you have the opportunity to evaluate this difference in the photos below.
Model train rail spacing dimensions
You can find a comparison image below for common rail spacing measurements.
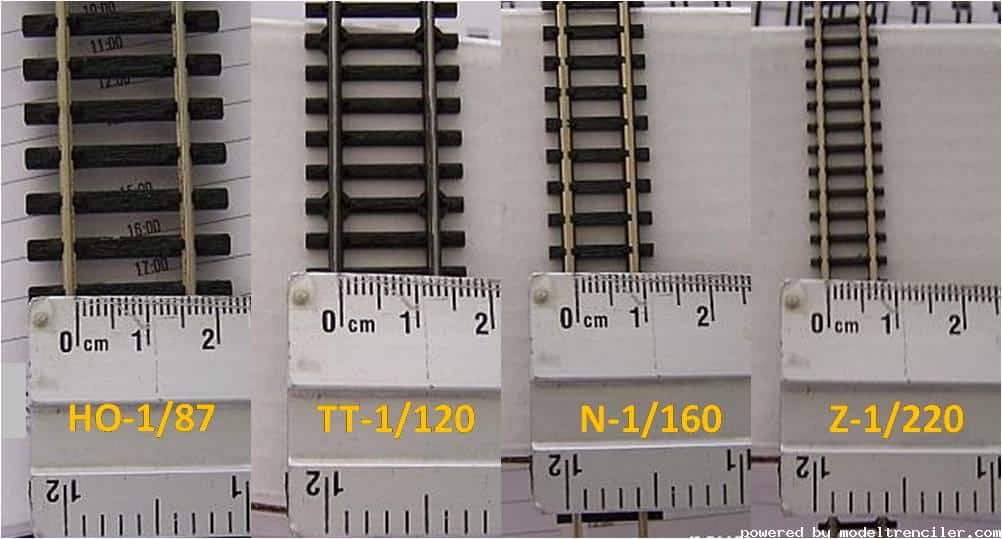
You can use the https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Model_railroad_scales for all information used for model train scales and for companies producing at these scales.
The track height (Track Code) indicates the height of the rails on the railway from the ground. Along with the height, the thickness also makes some difference. In real life, heavier / thicker rails are used on the main lines, and lighter rails are laid on the secondary roads.
Model rails are also available in different height rail types and are expressed in inches per the height of the rail from the top of the crossbar. While the rails produced by model train manufacturers are generally used at a single height and often different heights from company to company, some private companies also produce model rails of different heights.
Commonly used values are 100.83, 70, and 55. If you are making your main lines with Code 100 rails in a realistic setup, you should make the secondary/sidelines with code 83 rails. You can find the recommended values for rail heights and thicknesses at https://www.nmra.org/standards/
| Code Ray | Height (A) | Rail Thickness (C) |
| 100 | .100inç=2.54mm | 1.14mm |
| 83 | .083inç=2.10mm | 1.02mm |
| 70 | .070inç=1.78mm | 0.89mm |
| 55 | .055inç=1.40mm | 0.71mm |
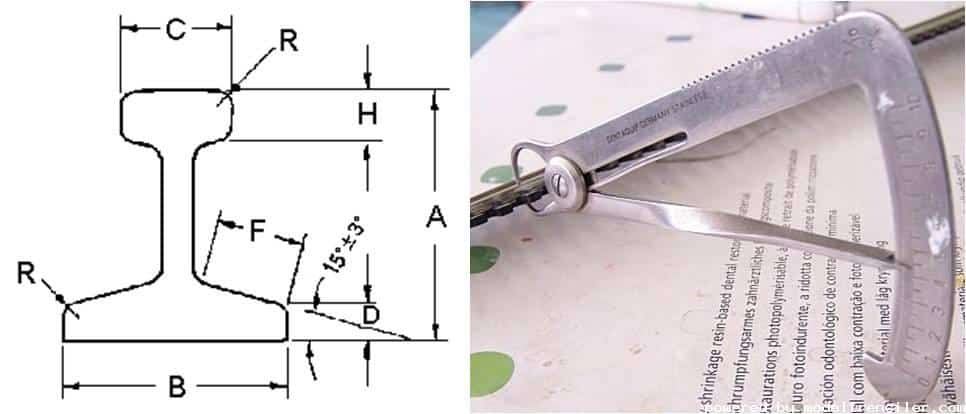
Height of Model Train Rail profiles
Rail profiles may have different heights for different manufacturers. In other words, one manufacturer can produce Code 100 rails while another can produce Code 83. For this reason, the height difference may arise between the rails of different manufacturers, but with a small filing process, the protrusion on the rail surface can be removed, and the transition adapters used by some manufacturers can be used.
Rail joiners (Fishplate / Joiner) are small metal or plastic parts that allow the rails to transmit electricity to each other. The metal ones of these parts make the rails united and electrically unified. In special applications such as understanding line usage, the method of cutting rails in some regions on the fiction or plastic connectors is used.

Model Train Scales: From Largest to Smallest
If you’re a model train enthusiast or someone looking to enter the fascinating world of miniature railroads, understanding model train scales is crucial. Model trains come in a variety of scales, each offering a unique experience. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you on a journey from the largest to the smallest model train scales, exploring their characteristics, popularity, and the joy they bring to hobbyists worldwide.
Model trains have been captivating enthusiasts for generations, replicating the charm and nostalgia of real railroads on a smaller scale. The first decision any hobbyist must make is choosing the appropriate scale for their layout. Let’s embark on a journey through the various model train scales, from the grandiose to the incredibly intricate.
G Scale – The Giant Amongst Trains
G Scale, also known as Garden Scale, is the largest of them all. These trains are often used in outdoor garden railways due to their impressive size. The ratio for G Scale is typically 1:22.5 or 1:29, making them perfect for creating realistic scenes with extensive landscapes and buildings.
O Scale – A Classic Favorite
O Scale is a classic favorite among model train enthusiasts. With a ratio of 1:48, these trains are larger than most and offer intricate details. They are commonly found around Christmas trees or as part of elaborate indoor layouts.
HO Scale – The Most Popular Choice
HO Scale is the most popular choice worldwide, with a ratio of 1:87.1. It strikes the perfect balance between size and detail, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced hobbyists. The wide availability of HO Scale accessories and models adds to its appeal.
N Scale – Compact Realism
N Scale enthusiasts appreciate the compact realism of these trains, with a ratio of 1:160. They are perfect for those with limited space for layouts but still want intricate and detailed trains.
Z Scale – The Miniature Marvel
Z Scale is known for its miniature marvels, boasting a tiny 1:220 ratio. These trains are perfect for those who want to create intricate scenes on a small tabletop layout.
TT Scale – A Rare Gem
TT Scale is a rare gem, with a ratio of 1:120. Falling between HO and N Scale, TT Scale offers a unique niche for collectors and modelers seeking something different.
Scale Comparison Chart
To help you visualize the differences between these scales, here’s a handy comparison chart:
| Scale | Ratio | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|
| G Scale | 1:22.5-1:29 | Garden Railways |
| O Scale | 1:48 | Indoor Layouts, Holidays |
| HO Scale | 1:87.1 | Versatile, Wide Selection |
| N Scale | 1:160 | Limited Space, Realism |
| Z Scale | 1:220 | Miniature Layouts |
| TT Scale | 1:120 | Unique Collectors’ Choice |
Choosing the Right Scale for You
Selecting the right scale depends on your space, budget, and personal preferences. Consider the amount of space you have available for your layout, your desired level of detail, and your preferred era of railroad modeling.
Building Your Model Train Layout
Building a model train layout is a rewarding experience. It allows you to create your miniature world, complete with landscapes, buildings, and even operational features like signals and crossings.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance is essential to keep your model trains running smoothly. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and track maintenance are vital to ensure years of trouble-free operation.
Collecting and Customizing
Many model train enthusiasts enjoy collecting vintage trains and customizing them to fit their vision. This aspect of the hobby allows for creativity and personalization.
The Thrill of Model Trains
The joy of model trains goes beyond the hobby itself. It’s about creating, sharing, and reliving the magic of railroads in a miniature world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, model train scales offer a diverse range of options for enthusiasts. Whether you prefer the grandeur of G Scale or the intricate detailing of Z Scale, there’s a scale that suits your interests and space. Start your journey into the world of model trains today and bring the magic of railroads to life in your own home.
FAQs
1. How do I choose the right scale for my model train layout?
Choosing the right scale depends on your available space, budget, and personal preferences. Consider these factors when making your decision.
2. What are the advantages of HO Scale?
HO Scale is popular due to its versatility and wide selection of accessories and models, making it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced hobbyists.
3. Can I combine different scales on one layout?
Combining scales can be challenging due to the differences in size, but with careful planning and creativity, it is possible to create unique layouts.
4. How do I maintain my model trains?
Regular cleaning, lubrication, and track maintenance are essential for maintaining the performance of your model trains.
5. Where can I find rare TT Scale models?
Rare TT Scale models can sometimes be found at specialized hobby shops, online marketplaces, or through collector’s networks.
Access Now: https://amzn.to/3LaIHcY
In this article, we’ve explored model train scales from the largest to the smallest, helping you understand the characteristics and appeal of each. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned enthusiast, choosing the right scale is the first step in creating your miniature railroad world. So, pick your scale, let your creativity flow, and enjoy the enchanting world of model trains.







