Overview of lacquer thinner
What is lacquer thinner?
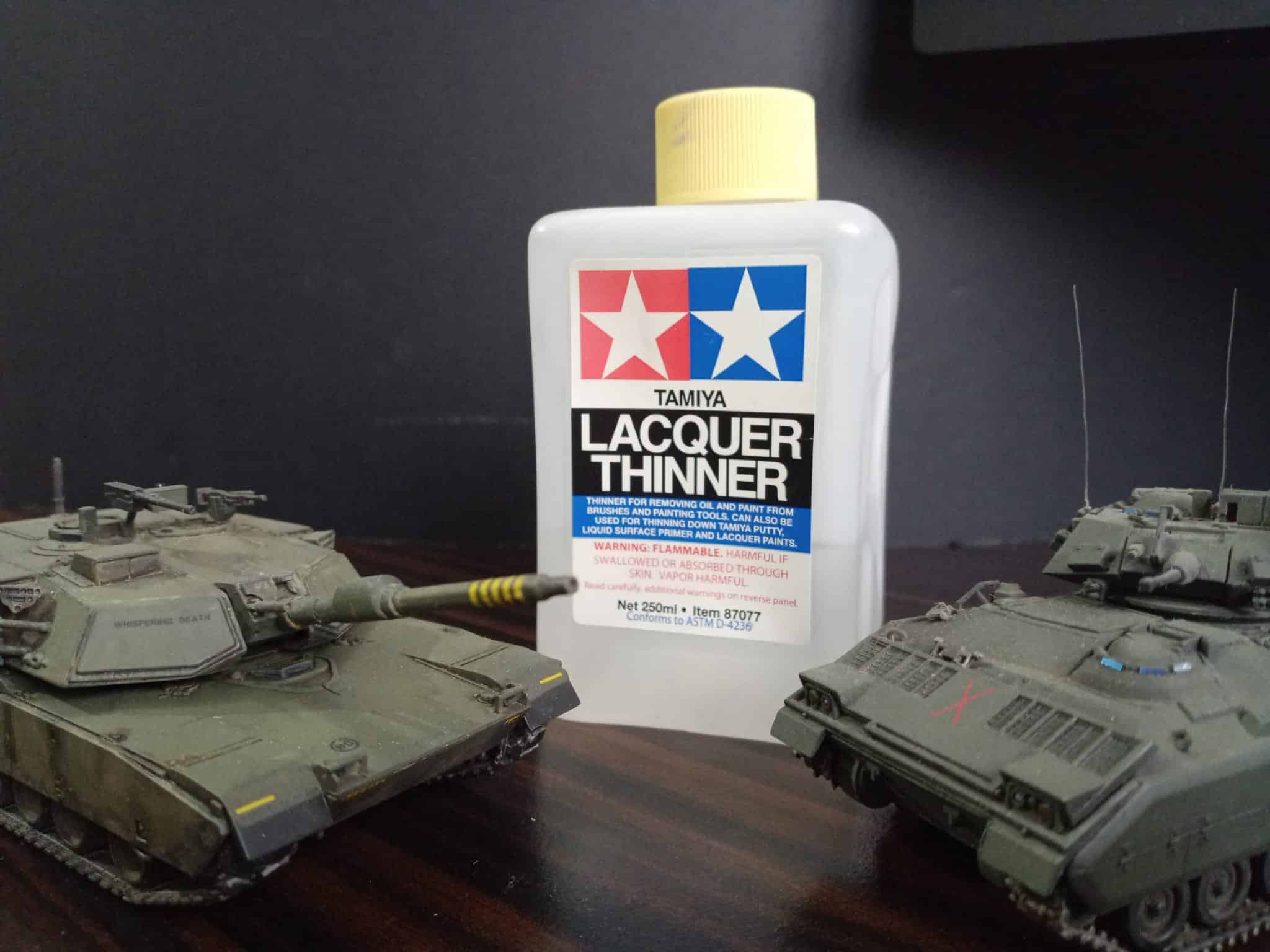
Lacquer thinner, also known as cellulose thinner, is a mixture of solvents used to dissolve lacquer paints and resins. It is a flammable liquid that evaporates quickly, which is why it is used to thin lacquer paints and make them easier to apply. Lacquer thinner can also be used to clean up lacquer paint spills and to remove dried lacquer paint from brushes and airbrushes.
Here are some of the properties of lacquer thinner:
- Flammable: Lacquer thinner is a flammable liquid and should be handled with care. It is important to keep it away from heat sources and open flames.
- Evaporates quickly: Lacquer thinner evaporates quickly, which is why it is used to thin lacquer paints. This also means that it can dry out quickly, so it is important to work in a well-ventilated area.
- Strong odor: Lacquer thinner has a strong odor, so it is important to use it in a well-ventilated area. It is also a good idea to wear a respirator or mask when using it.
Why Lacquer Thinners are Important?
A brief overview of lacquer thinners and their significance in model kit painting
Lacquer thinners are a crucial component in model kit painting, playing a vital role in achieving smooth, professional-looking finishes. They are specifically formulated to work with lacquer paints, which are known for their exceptional durability, fast drying times, and vibrant colors.
-
Thinning lacquer paints: Lacquer thinners are primarily used to thin lacquer paints, making them flow more easily through airbrushes and achieving a smoother, more even finish. The appropriate thinning ratio depends on the specific paint brand, airbrush setup, and desired paint consistency.
-
Cleaning airbrushes and painting tools: Lacquer thinners are effective in removing lacquer paint residue from airbrushes, brushes, and other painting tools. Proper cleaning ensures optimal performance and prevents paint buildup that could affect the quality of future painting sessions.
-
Removing unwanted paint: Lacquer thinners can be used to remove unwanted paint mistakes or to strip entire paint jobs from model kits. However, caution should be exercised as lacquer thinners can damage certain types of plastic, so it’s crucial to test the thinner on an inconspicuous area before applying it to the entire model.
-
Creating weathering effects: Lacquer thinners can be used to create weathering effects on model kits, such as fading paintwork or simulating chipped edges. This technique involves carefully applying diluted lacquer thinner to specific areas of the model to mimic the natural wear and tear of real-world vehicles or structures.
-
Enhancing paint adhesion: Lacquer thinners can be used to improve the adhesion of lacquer paints to certain surfaces, particularly resin or bare plastic. Thinning the paint with a small amount of lacquer thinner can enhance its flow and penetration into the surface, resulting in a more durable and long-lasting paint job.
Overall, lacquer thinners play a crucial role in model kit painting, providing versatility and enhancing the painting process. Their ability to thin paints, clean tools, remove unwanted paint, create weathering effects, and improve paint adhesion makes them indispensable tools for modelers who work with lacquer paints.
Tamiya Lacquer Paint Review – Tried and tested new paints

Highlighting the importance of using the right thinner for specific paints and applications
Using the right thinner for specific paints and applications is crucial for achieving desirable results and ensuring the longevity of your painting project. Each type of paint has unique properties that require a compatible thinner for optimal performance. Choosing the wrong thinner can lead to a variety of issues, including:
-
Incompatibility: Using an incompatible thinner can cause the paint to coagulate or separate, rendering it unusable.
-
Improper Drying: Incorrectly thinned paint may dry too quickly or too slowly, affecting the paint’s flow and finish.
-
Poor Adhesion: Improper thinning can compromise the paint’s adhesion to the surface, leading to peeling or flaking.
-
Color Alteration: Some thinners can react with the paint’s pigments, causing discoloration or fading.
To ensure successful painting outcomes, it is essential to select the appropriate thinner based on the type of paint and application:
Oil-Based Paints:
Oil-based paints require mineral spirits or turpentine as thinners. These solvents effectively reduce the paint’s viscosity, allowing for smooth application and achieving the desired gloss level.
Latex Paints:
Latex paints are best thinned with water. Water effectively lowers the paint’s viscosity without affecting its color or drying time.
Shellac and Lacquer Paints:
Shellac and lacquer paints require specialized thinners formulated specifically for these types of paints. These thinners ensure proper drying time and prevent the paint from becoming gummy or tacky.
Airbrushing:
Airbrushing demands a thinner mixture to achieve a fine mist and prevent clogging of the airbrush nozzle. Specific airbrush thinners are designed to provide the proper flow and drying characteristics for airbrushing applications.
Hand Painting:
Hand painting generally requires a slightly thicker mixture compared to airbrushing. This allows for better control over the paint application and prevents the paint from drying too quickly on the brush.
Environmental Considerations:
When selecting a thinner, consider the environmental impact of the product. Opt for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) or water-based thinners whenever possible to minimize harmful emissions and reduce environmental impact.
Consulting Instructions:
Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific recommendations on thinning ratios and compatible thinners for the paint you are using.
In conclusion, using the right thinner for specific paints and applications is paramount for achieving professional-looking results and ensuring the longevity of your painting project. By selecting the appropriate thinner based on the paint type, application method, and environmental considerations, you can optimize paint performance, prevent common issues, and contribute to a sustainable approach to painting.
Which Enamel thinner should I use?
Understanding Lacquer Thinners
Demystifying the composition and properties of lacquer thinners
Lacquer thinners are versatile solvents that play a crucial role in model kit painting, enabling smooth application, effective cleaning, and the creation of unique effects. They are typically composed of a mixture of solvents, each with distinct properties that contribute to the overall performance of the thinner.
- Acetone: A highly volatile solvent with strong dissolving power, acetone effectively thins lacquer paints and aids in cleaning.
- Toluene: A colorless aromatic hydrocarbon, toluene enhances the flow and leveling of lacquer paints, contributing to a smoother finish.
- Xylene: Another aromatic hydrocarbon, xylene shares similar properties to toluene, promoting paint flow and leveling while offering a slightly slower evaporation rate.
- Methanol (Methyl Alcohol): A highly flammable alcohol, methanol exhibits fast evaporation and aids in removing paint residues and cleaning equipment.
- N-Butanol: A higher-boiling alcohol, n-butanol provides slower evaporation compared to methanol, allowing for better paint flow and blending.
- Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA): Commonly known as rubbing alcohol, IPA is a versatile solvent used for cleaning, degreasing, and thinning lacquer paints.
Explaining the different types of lacquer thinners available and their unique characteristics
Advantages of Using Lacquer Thinners
- Enhancing paint flow and consistency for smooth application
- Achieving a flawless and even finish on model kits
- Promoting faster drying times for efficient painting
Disadvantages of Lacquer Thinners
- Potential for harming plastic components if used incorrectly
- Flammability and health hazards associated with lacquer thinners
- Importance of proper ventilation and safety precautions
Enamel vs Lacquer vs Acrylic Model Paints
Selecting the Right Lacquer Thinner for Your Needs
- Matching the thinner to the type of paint being used
- Considering the desired finish and drying time
- Consulting model kit instructions and paint manufacturer recommendations
Essential Tips for Using Lacquer Thinners Effectively
- Thinning paint in small increments to avoid over-thinning
- Using a well-ventilated area and wearing appropriate protective gear
- Testing the thinned paint on a scrap piece before applying it to the model kit
Common Techniques for Thinning Lacquer Paints
- Airbrush thinning: achieving a fine mist for delicate details
- Brush thinning: ensuring smooth and consistent brushstrokes
- Mixing ratios and guidelines for different paint types
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Lacquer Thinners
- Addressing paint that is too thin or too thick
- Resolving air bubbles or other imperfections in the paint finish
- Dealing with paint that dries too quickly or too slowly
How To Thin Acrylic Paint For Airbrush
Lacquer Thinners vs. Other Modeling Thinners
- Comparing lacquer thinners to enamel and acrylic thinners
- Understanding the strengths and limitations of each type of thinner
- Choosing the most suitable thinner for specific modeling projects
Safety Precautions for Handling Lacquer Thinners
- Avoiding skin contact and inhalation of lacquer thinner fumes
- Storing lacquer thinners in a safe and secure location
- Properly disposing of used lacquer thinner and contaminated materials
Environmental Considerations when Using Lacquer Thinners
- Minimizing the environmental impact of lacquer thinners
- Choosing eco-friendly alternatives when possible
- Practicing responsible disposal and recycling
Measuring paint and thinner to mix
Conclusion
- Recap of the essential aspects of using lacquer thinners for model kits
- Emphasizing the importance of proper selection, usage, and safety precautions
- Encouraging model kit enthusiasts to experiment and refine their thinning techniques
FAQs
-
What are the main differences between lacquer thinners, enamel thinners, and acrylic thinners?
-
How can I determine the appropriate thinning ratio for my specific paint and application?
-
What are some alternative, non-toxic thinners that can be used for model kits?
-
How can I safely dispose of used lacquer thinner and prevent environmental contamination?
-
What are some additional tips for achieving a professional-looking finish with lacquer thinners?